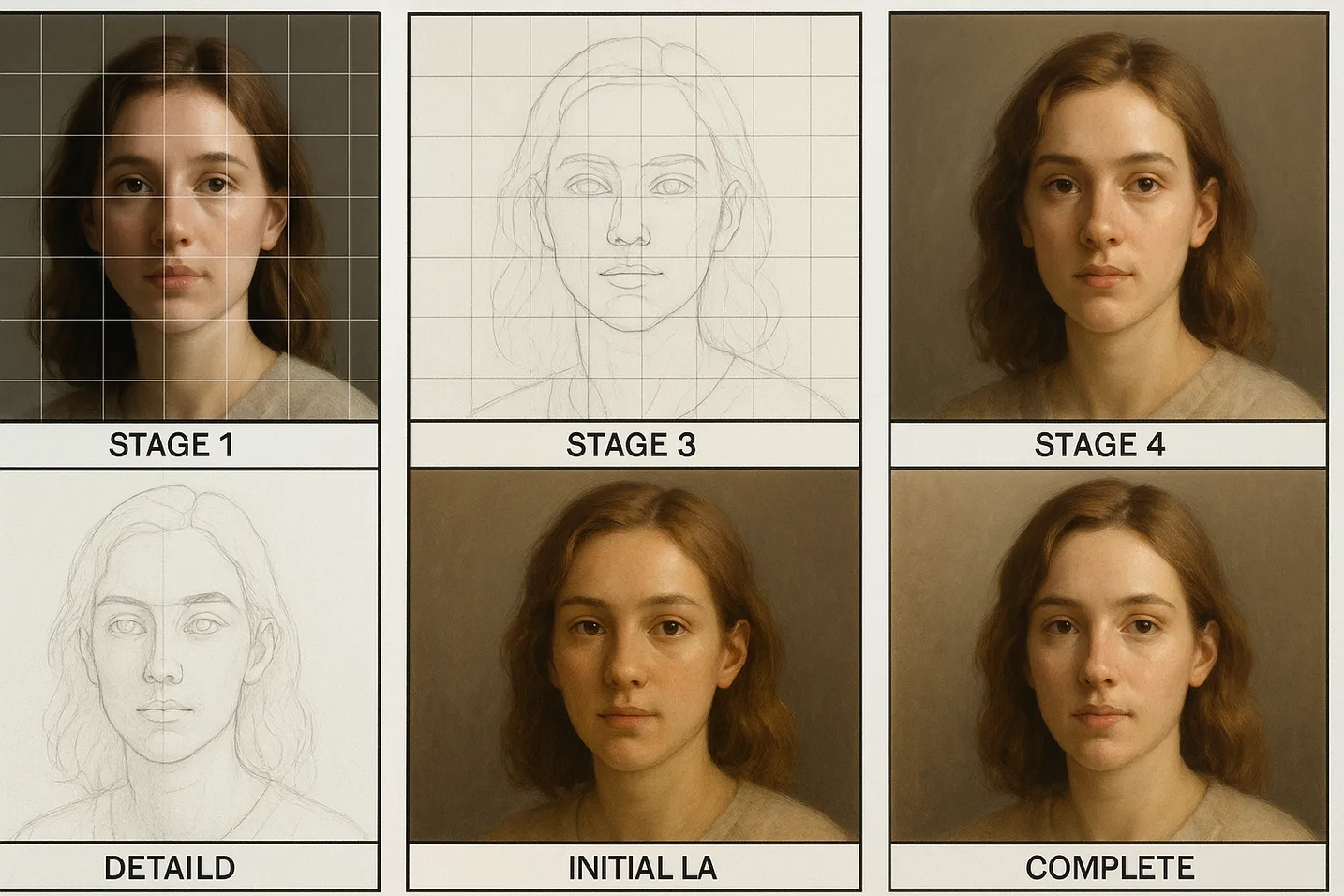
Portrait painting development requires systematic coordination between accurate drawing foundations and sophisticated painting techniques that build complexity progressively while maintaining likeness accuracy and artistic expression. Grid methods provide essential frameworks for coordinating initial construction with paint application, ensuring that technical excellence supports rather than constrains creative interpretation throughout the complete portrait development process. For comprehensive grid drawing fundamentals, explore our complete grid drawing guide.
My first commissioned portrait painting taught me harsh lessons about the relationship between drawing accuracy and painting success when I discovered that beautiful paint handling could not compensate for fundamental proportion errors established during initial construction. Despite competent painting techniques, the portrait failed to capture convincing likeness because the underlying drawing lacked the systematic accuracy necessary for successful portrait work. Learning to integrate grid construction methods with painting development transformed my approach, revealing how systematic foundations enable rather than constrain expressive painting techniques.
Portrait painting represents one of the most demanding artistic disciplines, requiring coordination between observational accuracy, technical painting skills, and expressive interpretation that serves both likeness capture and artistic vision. The most successful portrait painting approaches balance systematic construction with creative paint handling, ensuring that technical foundations support sophisticated artistic development throughout the complete working process.
Systematic Portrait Development Through Grid Integration
If you want to keep portrait proportions stable while you paint and refine, start from a gridded reference (create one with our image grid generator).
Foundation Drawing and Painting Coordination
Grid construction as painting preparation: Professional portrait painting begins with systematic drawing foundations that provide accuracy frameworks for subsequent paint application. Understanding how to coordinate grid construction with painting requirements prevents common problems that arise when drawing and painting approaches conflict rather than support each other.
Construction phase integration with paint planning:
- Value structure establishment: Using grid analysis to plan major light and shadow patterns
- Color temperature organization: Systematic approaches to warm and cool color distribution
- Edge quality planning: Understanding where edges should be hard, soft, or lost entirely
- Brushwork direction: Coordinating grid construction with intended paint application techniques
- Surface preparation: Ensuring drawing foundations support rather than interfere with painting materials
Proportion accuracy and likeness development: Portrait painting success depends heavily on proportion accuracy established during initial construction phases. Grid techniques ensure that fundamental relationships remain accurate throughout painting development, preventing likeness problems that become difficult to correct in advanced painting stages.
Professional Portrait Construction Methods
Academic drawing integration with painting development: Traditional portrait training emphasizes drawing accuracy as the foundation for painting success, using grid techniques to ensure proportion accuracy while developing painting skills that enhance rather than compromise drawing foundations.
Reference analysis and construction planning: Professional portrait work requires systematic reference analysis that identifies essential information for both drawing construction and painting development. Understanding how to extract maximum information from reference materials supports both accuracy and artistic interpretation.
Stage-by-stage development coordination:
- Initial construction: Grid-based drawing that establishes major relationships accurately
- Value development: Systematic light and shadow development building on accurate proportional foundations
- Color development: Temperature and chroma coordination supporting value structure and likeness
- Detail integration: Selective detail development that enhances rather than compromises overall unity
- Final refinement: Systematic completion approaches that maintain accuracy while achieving artistic goals
Advanced Portrait Painting Techniques with Grid Applications
Value Structure and Form Development
Systematic value planning through grid analysis: Professional portrait painting requires sophisticated value structure that creates convincing form while supporting likeness accuracy. Grid techniques help analyze and plan value relationships systematically, ensuring that light and shadow patterns enhance rather than contradict accurate proportional foundations.
Form modeling and dimensional development: Portrait painting must create convincing three-dimensional form through systematic value and color relationships. Understanding how to coordinate grid construction with form modeling enables portraits that appear dimensionally convincing while maintaining surface accuracy.
Light and shadow integration with systematic construction:
- Cast shadow accuracy: Ensuring shadow shapes support rather than contradict form structure
- Form shadows: Systematic development of shadows that reveal form while maintaining proportional accuracy
- Reflected light: Understanding how environmental light affects form appearance and portrait atmosphere
- Highlight placement: Strategic light accent placement that enhances form and surface character
- Atmospheric effects: Environmental conditions affecting light quality and portrait mood
Color Development and Temperature Control
Systematic color planning and temperature organization: Portrait painting requires sophisticated color relationships that create form, atmosphere, and artistic unity while maintaining likeness accuracy. Understanding how to coordinate color development with grid construction prevents common problems where color choices conflict with structural accuracy.
Flesh tone development and individual characteristics: Professional portrait painting must capture individual skin characteristics while maintaining systematic color relationships. Grid techniques help analyze and reproduce these characteristics accurately while supporting overall painting unity. Learn more about mastering the grid technique in drawing and painting.
Environmental integration and atmospheric effects:
- Background coordination: Systematic approaches to backgrounds that support rather than compete with portrait subjects
- Clothing integration: Appropriate treatment of costume elements that enhance portrait focus
- Lighting consistency: Maintaining unified light source effects throughout portrait development
- Color harmony: Overall color relationships that create unity while supporting individual character
- Artistic interpretation: Creative color choices that enhance rather than compromise likeness accuracy
Professional Portrait Applications and Career Development
Commission Work and Client Relationships
Professional standards and client expectations: Portrait painting careers require understanding client expectations while maintaining artistic integrity and technical standards. Grid techniques provide systematic approaches that demonstrate professionalism while ensuring accuracy that satisfies both artistic and commercial requirements.
Communication and approval processes: Professional portrait work involves systematic client communication throughout development phases, requiring approaches that demonstrate progress while maintaining quality control and artistic direction.
Pricing and business considerations:
- Time estimation: Understanding how systematic approaches affect project timeline and pricing
- Quality guarantees: Systematic methods that enable consistent quality across different commissions
- Revision procedures: Professional approaches to client feedback and modification requests
- Portfolio development: Creating work that demonstrates both technical competency and artistic vision
- Professional presentation: Systematic documentation and presentation of portrait work for career advancement
Educational and Instructional Applications
Teaching portrait painting systematically: Portrait instruction requires combining technical knowledge with effective communication skills. Understanding how to demonstrate systematic construction methods while maintaining focus on artistic development serves educational opportunities and professional growth.
Workshop development and specialized instruction: Portrait painting workshops provide opportunities for sharing systematic knowledge while generating additional income streams. Understanding how to design effective instruction that combines technical accuracy with artistic development requires both expertise and teaching ability.
Professional development and continuing education:
- Master class participation: Advanced instruction from accomplished practitioners
- Academic study: Formal education in portrait painting methods and art history
- Museum study: Learning from masterworks through systematic analysis and copying
- Peer learning: Professional networks supporting continued development and knowledge sharing
- Research integration: Incorporating contemporary understanding into traditional portrait methods
Specialized Portrait Categories and Technical Approaches
Children's Portraits and Age-Specific Considerations
Proportional adaptation for different ages: Children's portraits require adapted grid approaches that accommodate different proportional relationships while maintaining accuracy and capturing age-appropriate characteristics. Understanding developmental proportions enables portraits that appear authentically childlike rather than miniaturized adults.
Capture challenges and behavioral considerations: Children's portraits often involve working from limited reference material due to attention span and behavioral constraints. Systematic approaches help maximize information extraction from available references while maintaining portrait quality.
Family portraits and group coordination:
- Multiple subject coordination: Systematic approaches to maintaining individual accuracy within group compositions
- Scale relationships: Ensuring appropriate size relationships between subjects of different ages
- Compositional unity: Creating unified group presentations while maintaining individual character
- Lighting consistency: Managing complex lighting across multiple subjects and spatial positions
- Interactive relationships: Capturing family dynamics and relationships through systematic construction
Historical and Period Portrait Work
Research and historical accuracy considerations: Historical portrait work requires understanding period-appropriate representation while maintaining systematic accuracy. Research into historical costume, pose conventions, and cultural contexts informs systematic construction approaches.
Material and technique coordination: Different historical periods employed different materials and techniques that affect portrait appearance. Understanding how to adapt systematic approaches for historical accuracy while maintaining contemporary technical standards serves specialized career applications.
Cultural sensitivity and appropriate representation:
- Period accuracy: Appropriate representation of historical subjects within cultural contexts
- Research methodology: Systematic approaches to historical reference gathering and verification
- Contemporary standards: Balancing historical accuracy with current expectations for respectful representation
- Client education: Communicating historical context and artistic choices to contemporary audiences
- Professional ethics: Maintaining appropriate standards when representing historical subjects and cultural contexts
Digital Integration and Contemporary Portrait Methods
Technology-Enhanced Portrait Development
Digital reference preparation and analysis: Contemporary portrait painting benefits from digital tools that enhance reference analysis and preparation while supporting traditional painting execution. Understanding how to integrate these technologies maintains painting skill development while improving efficiency and accuracy.
Hybrid workflows and systematic integration: Many professional portrait artists combine digital analysis with traditional execution methods. Understanding how to coordinate these approaches maximizes both efficiency and artistic quality while maintaining essential hands-on painting skills.
Documentation and presentation technologies:
- Progress documentation: Digital recording of systematic development processes for client communication and artistic analysis
- Portfolio enhancement: Professional digital presentation of traditional portrait work
- Client communication: Effective sharing of work progress and artistic decision-making processes
- Educational applications: Creating instructional content demonstrating systematic portrait development
- Professional networking: Using documentation for career development and professional relationship building
Contemporary Market Applications
Fine art and gallery representation: Contemporary portrait painting careers often involve gallery representation requiring sophisticated work that demonstrates both technical competency and individual artistic vision through systematic skill development combined with creative interpretation.
Commercial applications and professional services: Portrait painting serves diverse commercial applications including corporate commissions, family portraits, and commemorative work requiring systematic approaches that enable efficient production while maintaining artistic quality and client satisfaction.
Competition and exhibition opportunities:
- Portrait societies: Professional organizations supporting portrait painting excellence and career development
- Competition standards: Understanding judging criteria and quality expectations for portrait competitions
- Exhibition preparation: Systematic approaches to preparing work for professional presentation
- Awards and recognition: Building professional reputation through systematic excellence and artistic achievement
- International opportunities: Understanding global portrait painting communities and career possibilities
Problem-Solving Complex Portrait Challenges
Technical Problem Resolution
Likeness challenges and correction methods: Even systematic construction approaches can encounter likeness problems requiring systematic diagnosis and correction. Understanding how to identify and address these issues maintains portrait quality while supporting continued artistic development.
Reference material limitations and solutions: Portrait painting often involves working with less-than-ideal reference materials requiring systematic approaches to information extraction and interpretation while maintaining portrait quality and likeness accuracy.
Material and technique coordination challenges:
- Paint handling: Coordinating systematic construction with expressive paint application techniques
- Surface preparation: Ensuring drawing foundations support rather than interfere with painting materials
- Drying time management: Coordinating wet and dry painting techniques with systematic construction schedules
- Color mixing: Systematic approaches to color preparation and consistency throughout extended painting sessions
- Brush selection: Choosing appropriate tools for different construction and painting phases
Creative and Artistic Challenges
Style development and artistic voice: Professional portrait painting requires developing individual artistic voice while maintaining systematic technical competency. Understanding how to integrate personal expression with systematic accuracy serves long-term artistic development and career sustainability.
Creative interpretation and artistic enhancement: Successful portrait painting often involves creative choices that enhance rather than simply copy reference materials. Systematic construction provides foundations that enable confident creative interpretation while maintaining likeness accuracy.
Client collaboration and artistic direction:
- Vision communication: Effectively sharing artistic concepts and technical approaches with clients
- Feedback integration: Systematic approaches to incorporating client input while maintaining artistic integrity
- Expectation management: Professional communication about artistic processes and timeline requirements
- Creative leadership: Guiding clients toward artistic solutions that serve both their needs and artistic excellence
- Long-term relationships: Building client relationships that support continued artistic development and business growth
Career Development and Professional Growth
Advanced Skill Development
Master class study and advanced instruction: Professional portrait painting careers benefit from continued advanced study with accomplished practitioners. Understanding how to identify and pursue appropriate educational opportunities supports continued artistic development and professional growth.
Research and scholarly applications: Some portrait painters pursue research into historical methods, materials, and techniques that inform contemporary practice while contributing to artistic knowledge and professional recognition.
International study and cultural exchange:
- Residency programs: Opportunities for intensive study and cultural exchange that inform artistic development
- Museum study: Learning from masterworks through systematic analysis and copying in major collections
- Cross-cultural learning: Understanding different portrait traditions and their integration with systematic approaches
- Language development: Communication skills supporting international artistic opportunities and relationships
- Cultural sensitivity: Appropriate engagement with different artistic traditions and cultural contexts
Business Development and Professional Practice
Practice establishment and client development: Professional portrait painting requires business skills including marketing, client relations, and project management that coordinate with artistic excellence to create sustainable career practices.
Professional networking and industry relationships: Successful portrait careers often depend on professional relationships with galleries, collectors, and other artists that support both artistic development and business opportunities.
Long-term career planning and development:
- Skill progression: Systematic approaches to continued artistic development throughout career phases
- Market adaptation: Understanding changing client needs and artistic trends while maintaining technical excellence
- Teaching integration: Developing instructional capabilities that provide additional income while supporting artistic community
- Legacy development: Creating work and knowledge that contributes to artistic tradition and cultural development
- Mentorship opportunities: Sharing systematic knowledge with developing artists while supporting artistic community growth
Mastering Portrait Painting Excellence Through Systematic Development
From sketch to masterpiece using the grid method for portrait painting represents sophisticated integration of systematic construction methods, professional painting techniques, and artistic sensitivity that serves both technical excellence and creative expression. Through consistent application of grid techniques combined with painting skill development, artists create portraits that achieve both likeness accuracy and artistic distinction while building sustainable professional practices.
My experience with systematic portrait development has taught me that technical excellence provides foundations for rather than constraints on artistic expression, enabling confident creative choices while ensuring professional quality that satisfies both artistic goals and client expectations. The most accomplished portrait painters combine systematic construction knowledge with individual artistic vision, using grid methods as tools for achieving portrait goals rather than restrictions on creative interpretation.
Professional portrait painting success depends on understanding how systematic construction methods, painting techniques, and artistic sensitivity work together to create compelling visual representations that serve both artistic expression and professional application requirements. Through dedicated study and systematic application of grid techniques combined with painting skill development, artists develop the sophisticated technical abilities and artistic sensitivity necessary for lifelong growth in portrait painting and related professional applications.
Mastering Systematic Portrait Painting
For further study, explore portrait grid method and grid anatomy tips.
Ready to Try the Grid Method?
Put these techniques into practice with our free grid generator tool—trusted by 170,000+ artists worldwide.
Create Your Grid Now →