The Influence of Grids in Classical Drawing Techniques
Discover the timeless precision and proportional excellence of classical drawing with the grid method. Explore its historical roots, master key techniques, and see why this indispensable tool remains crucial in art education today. Dive in and elevate your artistry!

The Influence of Grids in Classical Drawing Techniques
In the realm of classical drawing, one method has persistently proven itself indispensable: the grid method. Though seemingly simplistic, the implementation of grids in drawing is far from rudimentary. With roots stretching back to the Renaissance, the grid method has influenced how artists sketch, refine, and define their works with unparalleled precision. This post aims to delve deep into the historical roots, elaborate on the techniques involved, and elucidate why grids are still pivotal in art education today.
A Historical Perspective of the Grid Method
To appreciate the profound influence of the grid method, it's imperative to first understand its historical context. The use of grids can be traced back to Ancient Egypt, where artists utilized proportional grids to maintain consistency in large-scale works such as murals and statues. Fast forward to the Renaissance, and we see notable artists like Leonardo da Vinci and Albrecht Dürer employing the grid method to achieve meticulous accuracy in their compositions.
The Renaissance, often regarded as the golden era of classical drawing, heralded the grid method as an essential technique for ensuring correct proportions and perspective. Da Vinci's famed "Vitruvian Man", for instance, exemplifies the harmony and precision made possible through the use of grids. During this period, artists began to formally teach the grid method in art education, laying a foundation that persists today.
Techniques: Mastering the Grid Method
Utilizing the grid method in classical drawing involves several steps, each crucial in transforming a sketch from a rudimentary outline into a detailed masterpiece. The process begins with selecting an appropriate reference image and superimposing a grid upon it. Typically, the grid comprises equal-sized squares, chosen based on the complexity and required detail of the final drawing.
Step 1: Choosing Your Grid
Choose the size of the grid based on the level of detail you need. Smaller, more intricate artworks may require grids with smaller squares, while larger compositions might benefit from fewer, larger squares.
Step 2: Creating the Grid on Your Drawing Surface
Transfer a grid of the same proportions onto your drawing paper. Ensure both grids (on the reference image and the drawing paper) are identical in size and number of squares. Consistency is key here, as any deviation might lead to inaccuracies.
Step 3: Detailed Sketching with Grids
Begin the sketching process. Focus on one square at a time, replicating the details from the corresponding square on the reference image. This division allows you to manage the complexity of the drawing, ensuring that each section is proportionately accurate.
Integration of Grids in Art Education
Art education, both historically and in contemporary settings, continues to emphasize the grid method due to its versatility and effectiveness. Introducing budding artists to grid techniques fosters an understanding of proportion and spatial relationships—fundamental concepts in classical drawing.
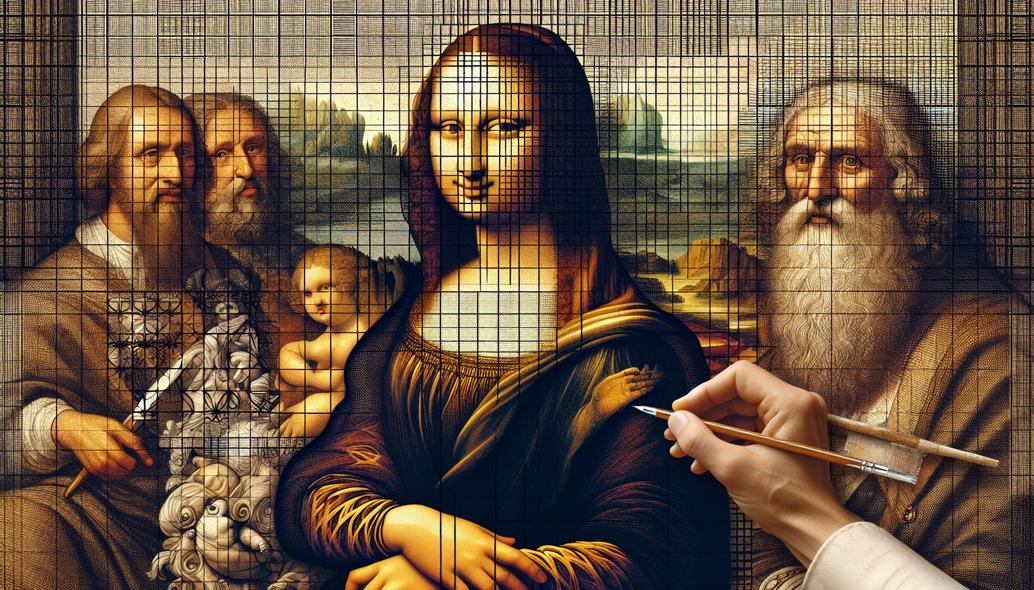
Early art education programs incorporate grid exercises, teaching students to deconstruct complex images into manageable segments. As they progress, students learn to apply grids not only as a form of direct replication but as a guide to freehand sketching, internalizing the concepts of proportion and spatial fidelity.
Grids: Beyond Classical Drawing
While rooted in classical techniques, the grid method transcends traditional boundaries, finding relevance in various modern applications. Graphic design, animation, and even digital art leverage grids to create structured and proportionate compositions. This intersection of classical techniques with contemporary practices underscores the grid method's enduring significance.
Grids in Graphic Design
In graphic design, grids help structure layouts, ensuring elements are aligned and proportionate. Designers often use grids to balance visual elements, improving aesthetics and functionality.
Grids in Animation and Digital Art
In the realms of animation and digital art, grids facilitate consistent character proportions and background design. By maintaining uniformity, animators and digital artists can create cohesive visual narratives.
Conclusion: The Timelessness of Grids in Drawing
The grid method, steeped in history and refined through centuries, remains a cornerstone of classical drawing techniques. From the grand frescoes of the Renaissance to the precise illustrations of contemporary graphic design, grids continue to guide artists towards precision and proportionality. Their integration into art education ensures that new generations of artists grasp foundational principles that are essential for both classical and modern applications.
In this ever-evolving art world, the grid method stands as a testament to the timelessness of fundamental techniques. Whether you are an aspiring artist taking your first steps or a seasoned professional refining your craft, the grid method provides a reliable framework upon which artistic excellence can be built.
Engage with grids, explore their potential, and witness how this classic technique can elevate your artwork to new heights of precision and beauty.
